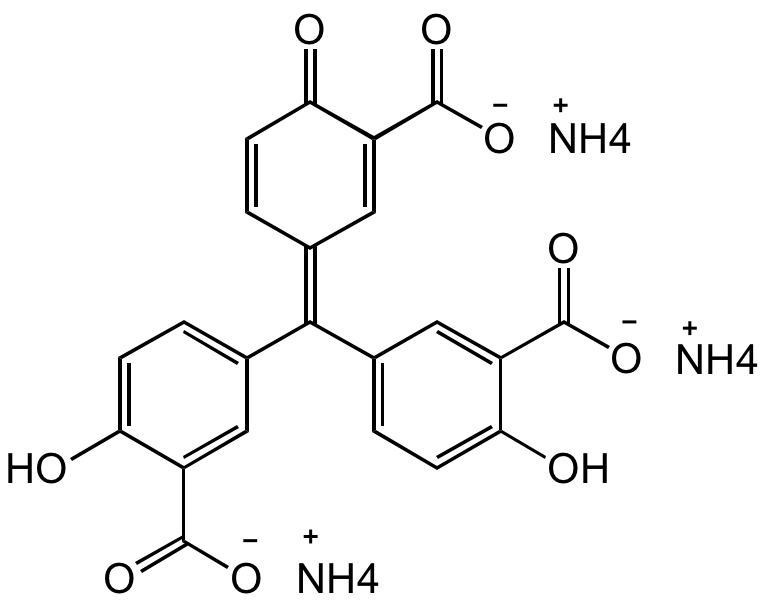
Aluminon
Product Code:
CDX-A0293
CDX-A0293
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
+20°C
+20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-A0293-G025 | 25 g | £65.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Aurintricarboxylic acid ammonium salt; ATA; Ammonium aurintricarboxylate
Appearance:
Dark red to brown powder.
CAS:
569-58-4
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C22H14O9.3H3N/c23-16-4-1-10(7-13(16)20(26)27)19(11-2-5-17(24)14(8-11)21(28)29)12-3-6-18(25)15(9-12)22(30)31;;;/h1-9,23-24H,(H,26,27)(H,28,29)(H,30,31);3*1H3
InChiKey:
AIPNSHNRCQOTRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 569-58-4. Formula: C22H14O9 . 3NH3. MW: 422.3 . 51.1. Synthetic. Aluminon, the triammonium salt of aurintricarboxylic acid, is a dye commonly used to detect the presence of the aluminium ion in an aqueous solution. In addition to its use in qualitative inorganic analysis, aluminon has applications in pigment production. It forms brilliantly colored lake pigments with aluminum, chromium, iron and beryllium. Spectral data: AL-Complex Absorbance at ~525nm. Aurintricarboxylic acid readily polymerizes in aqueous solution, forming a stable free radical that inhibits protein-nucleic acid interactions. It is a potent inhibitor of RNA-directed DNA polymerase and topoisomerase II. Angiogenesis inhibitor. It stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation processes including the Jak2/STAT5 pathway in NB2 lymphoma cells, ErbB4 in neuroblastoma cells, and MAP kinases, Shc proteins, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase and phospholipase C in PC12 cells. Aurintricarboxylic acid inhibits apoptosis in many cell types. It is neuroprotective maybe due to calpain inhibition. It has antiviral properties, is a potent phosphofructokinase inhibitor, a TWEAK-Fn14 signaling pathway inhibitor and a DNMT1 inhibitor.
MDL:
MFCD00040925
Molecular Formula:
C22H14O9 . 3NH3
Molecular Weight:
422.3 . 51.1
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Aluminon, the triammonium salt of aurintricarboxylic acid, is a dye commonly used to detect the presence of the aluminium ion in an aqueous solution. In addition to its use in qualitative inorganic analysis, aluminon has applications in pigment production. It forms brilliantly colored lake pigments with aluminum, chromium, iron and beryllium. Spectral data: AL-Complex Absorbance at ~525nm. Aurintricarboxylic acid readily polymerizes in aqueous solution, forming a stable free radical that inhibits protein-nucleic acid interactions. It is a potent inhibitor of RNA-directed DNA polymerase and topoisomerase II. Angiogenesis inhibitor. It stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation processes including the Jak2/STAT5 pathway in NB2 lymphoma cells, ErbB4 in neuroblastoma cells, and MAP kinases, Shc proteins, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase and phospholipase C in PC12 cells. Aurintricarboxylic acid inhibits apoptosis in many cell types. It is neuroprotective maybe due to calpain inhibition. It has antiviral properties, is a potent phosphofructokinase inhibitor, a TWEAK-Fn14 signaling pathway inhibitor and a DNMT1 inhibitor.
Purity:
n.a.
SMILES:
OC1=CC=C(/C(C2=CC=C(O)C(C([O-])=O)=C2)=C3C=C(C([O-])=O)C(C=C/3)=O)C=C1C([O-])=O.[NH4+].[NH4+].[NH4+]
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO or water (50mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT.
Documents
References
(1) G.R. Berube, et al.; Stain Technol. 39, 337 (1964) | (2) M.L. Stewart, et al.; PNAS 68, 97 (1971) (3) Blumenthal & T.A. Landers; BBRC 55, 680 (1973) | (4) J.F. Givens & K.F. Manly; Nucleic Acids Res. 3, 405 (1976) | (5) R.G. Gonzalez, et al.; Biochemistry 19, 4299 (1980) | (6) R.A Clark & G.L. Krueger; J. Histochem. Cytochem. 33, 729 (1985) (Review) | (7) J. Balzarini, et al.; BBRC 136, 64 (1986) | (8) S.A. McCune, et al.; Biochem. J. 259, 925 (1989) | (9) D. Schols, et al.; PNAS 86, 3322 (1989) | (10) I. Oberbaumer & C. Speth; Anal. Biochem. 185, 77 (1990) | (11) A.R. Gagliardi & D.C. Collins; Anticancer Res. 14, 475 (1994) | (12) D.R. Catchpoole & B.W. Stewart; Anticancer Res. 14, 853 (1994) | (13) Y. Benchokroun, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 49, 305 (1995) | (14) A. Posner, et al.; Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 36, 291 (1995) | (15) C.J. Tsi, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 62, 90 (2002) | (16) C.W. Chen, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 137, 1011 (2002) | (17) R. He, et al.; BBRC 320, 1199 (2004) | (18) H. Cho, et al.; Mol. Cells 18, 46 (2004) | (19) Y. Chen, et al.; Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 20, 19 (2009) | (20) J. Yoo, et al.; Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 87, 219 (2012) (Review) | (21) A. Roos, et al.; Oncotarget 8, 12234 (2017)