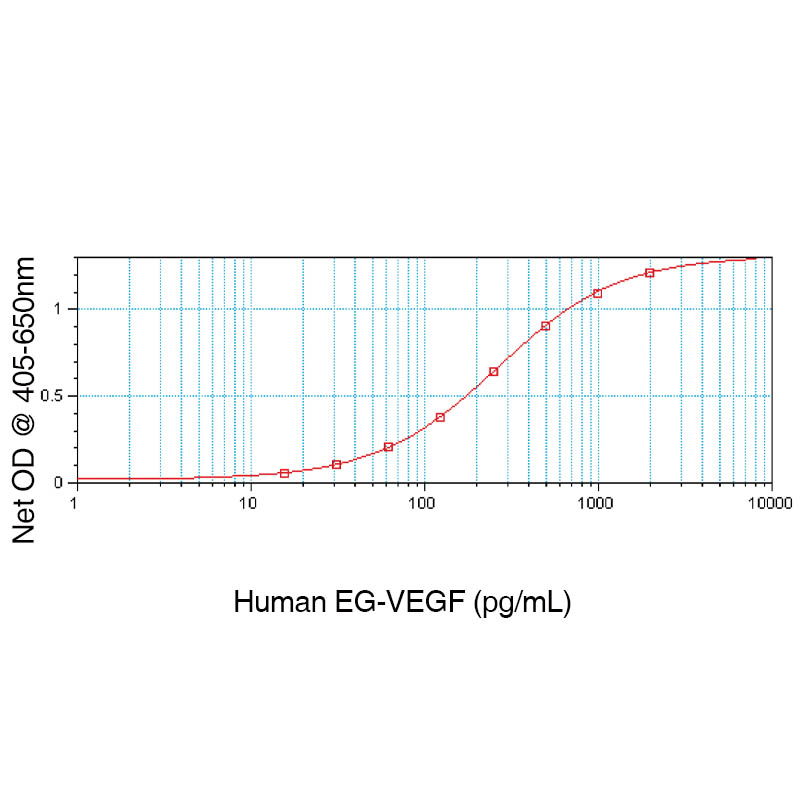
Human EG-VEGF ELISA Development Kit
Product Code:
LEI-E148
LEI-E148
Host Type:
Human
Human
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Application:
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| LEI-E148-15plates | 15 plates | £1,069.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT