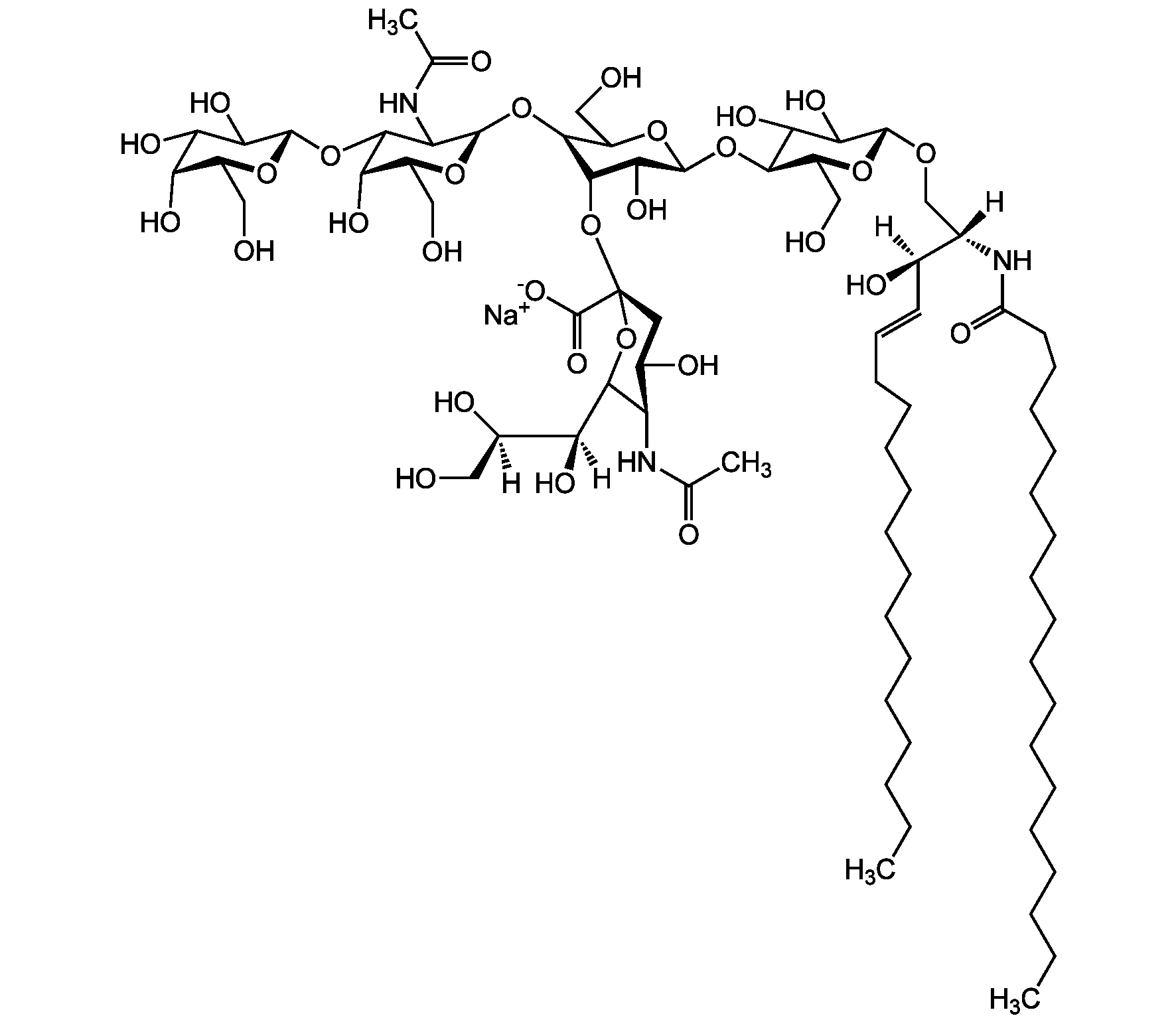
Ganglioside GM1 . sodium salt (bovine brain)
Product Code:
AG-CN2-9000
AG-CN2-9000
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-9000-M001 | 1 mg | £90.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-9000-M005 | 5 mg | £270.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-9000-M010 | 10 mg | £420.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
GM1 . Na; Monosialoganglioside GM1 . Na
CAS:
37758-47-7
EClass:
32160000
Endotoxin:
Not detectable.
Form (Short):
liquid
Formulation:
Lyophilized.
Handling Advice:
Hygroscopic.Protect from moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C73H131N3O31.Na/c1-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-19-20-22-24-26-28-30-32-34-52(87)76-44(45(84)33-31-29-27-25-23-21-18-16-14-12-10-8-6-2)41-98-69-61(94)59(92)63(50(39-80)101-69)103-71-62(95)67(107-73(72(96)97)35-46(85)53(74-42(3)82)66(106-73)55(88)47(86)36-77)64(51(40-81)102-71)104-68-54(75-43(4)83)65(57(90)49(38-79)99-68)105-70-60(93)58(91)56(89)48(37-78)100-70;/h31,33,44-51,53-71,77-81,84-86,88-95H,5-30,32,34-41H2,1-4H3,(H,74,82)(H,75,83)(H,76,87)(H,96,97);/q;+1/p-1/b33-31+;/t44-,45+,46?,47+,48?,49?,50?,51?,53+,54?,55-,56-,57-,58?,59?,60?,61?,62?,63+,64-,65?,66?,67?,68+,69+,70-,71-,73-;/m0./s1
InChiKey:
LFNNYGUBFYVSKX-FPEJYKFLSA-M
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 37758-47-7. Formula: C73H130N3O31 . Na. MW: 1545.8 . 23.0 (calculated on sphingosine C18:1 and stearic acid). Isolated from bovine brain. Gangliosides are acidic glycosphingolipids that form lipid rafts in the outer leaflet of the cell plasma membrane, especially in neuronal cells in the central nervous system. They participate in cellular proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, signal transduction, cell-to-cell interactions, tumorigenesis and metastasis. The accumulation of gangliosides has been linked to several diseases. Ganglioside GM1 is a major sialoglycolipid of neuronal membranes that modulates calcium homeostasis and which is important for neuronal plasticity and repair mechanisms. It binds to cholera toxin B subunit, resulting in stimulation of adenylyl cyclase in a wide variety of cell types. After cholera toxin binds to membrane associated Monosialoganglioside GM1, the A subunit of cholera toxin is translocated to the cell interior, where it catalyzes the ADP ribosylation of the membrane associated Gs subunit of adenylyl cyclase. In addition, binding of cholera toxin to monosialoganglioside GM1 causes translocation of NF-kappaB and activation of dendritic cells. E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) is structurally and functionally similar to cholera toxin and binds GM1 as well. GM1 has also been shown to improve Parkinson's disease symptoms and slow it's progression.
MDL:
MFCD00466936
Molecular Formula:
C73H130N3O31 . Na
Molecular Weight:
1545.8 . 23.0 (calculated on sphingosine C18:1 and stearic acid)
Package Type:
Glass Vial
Product Description:
Gangliosides are acidic glycosphingolipids that form lipid rafts in the outer leaflet of the cell plasma membrane, especially in neuronal cells in the central nervous system. They participate in cellular proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, signal transduction, cell-to-cell interactions, tumorigenesis and metastasis. The accumulation of gangliosides has been linked to several diseases. Ganglioside GM1 is a major sialoglycolipid of neuronal membranes that modulates calcium homeostasis and which is important for neuronal plasticity and repair mechanisms. It binds to cholera toxin B subunit, resulting in stimulation of adenylyl cyclase in a wide variety of cell types. After cholera toxin binds to membrane associated Monosialoganglioside GM1, the A subunit of cholera toxin is translocated to the cell interior, where it catalyzes the ADP ribosylation of the membrane associated Gs subunit of adenylyl cyclase. In addition, binding of cholera toxin to monosialoganglioside GM1 causes translocation of NF-kappaB and activation of dendritic cells. E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) is structurally and functionally similar to cholera toxin and binds GM1 as well. GM1 has also been shown to improve Parkinson's disease symptoms and slow it's progression.
Purity:
>98% (TLC)
Sequence:
Structure: II3Neu5AcGgOse4Cer; beta-Gal-(1-3)-beta-GalNAc-(1-4)-[alpha-Neu5Ac-(2-3)-]beta-Gal-(1-4)-beta-Glc-(1-1)-Cer; Cer: Sphingosine C18:1-C20:1, ~1:1 to 1:3 by vol.; stearic acid over 90%
SMILES:
[Na+].[H][C@@](O)(CO)[C@]([H])(O)C1O[C@@](CC(O)[C@H]1NC(C)=O)(O[C@@H]1C(O)[C@H](O[C@H]2C(O)C(O)[C@H](OC[C@]([H])(NC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)[C@]([H])(O)C=CCCCCCCCCCCCCC)O[C@H]2CO)OC(CO)[C@@H]1O[C@H]1O[C@@H](CO)[C@H](O)C(O[C@@H]2O[C@@H](CO)[C@H](O)C(O)C2O)C1NC(C)=O)C([O-])=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water (micellar aggregates) or chloroform:methanol (2:1).
Source / Host:
Isolated from bovine brain.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352211
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
Role of membrane gangliosides in the binding and action of bacterial toxins: P.H. Fishman; J. Membr. Biol. 69, 85 (1982) | Promotion of neuritogenesis in mouse neuroblastoma cells by exogenous gangliosides. Relationship between the effects and the cells association of ganglioside GM1: L. Facci, et al.; J. Neurochem. 42, 299 (1984) | A bacterium lipopolysaccharide that elicits Guillain-Barr? syndrome has a GM1 ganglioside-like structure: N.Yuki, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 178, 1771 (1993) | Ganglioside GM1 binds to the Trk protein and regulates receptor function: T. Mutoh, et al.; PNAS 92, 5087 (1995) | Dynamic and structural properties of sphingolipids as driving force to the formation of membrane domains: S. Sonnino, et al.; Chem. Rev. 106, 2111 (2006) | GM1 ganglioside in Parkinson's disease: Results of a five year open study: J.S. Schneider, et al.; J. Neurol. Sci. 292, 45 (2010) | Heat-Labile Enterotoxin: Beyond GM1 Binding: B. Mudrak & M.J. Kuehn; Toxins 2, 1445 (2010) | New findings on nuclear gangliosides: overview on metabolism and function: R. Ledeen & G.Wu; J. Neurochem. 116, 714 (2011) | Binding of CFA/I pili of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to Asialo-GM1 is mediated by the minor pilin CfaE: T.P. Madhavan, et al.; Infect. Immun. 84, 1642 (2016) | Phenotypic Analysis Reveals that the 2010 Haiti Cholera Epidemic Is Linked to a Hypervirulent Strain: K.J.F. Satchell, et al.; Infect. Immun. 84, 2473 (2016)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Ganglioside GD1a . disodium salt (bovine brain) | AG-CN2-9003 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganglioside GQ1b . tetrasodium salt (bovine brain) | AG-CN2-9007 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||