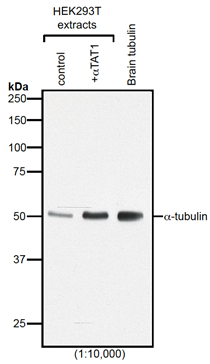
anti-alpha-Tubulin (acetylated) mAb (TEU318)
Product Code:
AG-20B-0068
AG-20B-0068
Antibody Isotype:
Mouse IgG1
Mouse IgG1
Antibody Clonality:
Monoclonal
Monoclonal
Antibody Clone:
TEU318
TEU318
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Target Species:
Universal
Universal
Applications:
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
-20°C
-20°C
Storage:
-20°C
-20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-20B-0068-C100 | 100 ug | £301.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges to UK mainland customers, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Concentration:
1mg/ml
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Formulation:
Liquid. In PBS containing 10% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide.
Handling Advice:
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C.Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Immunogen:
Tubulin of the Ciliate Euplotes eluted from the 55kDa band of SDS gel.
Long Description:
Monoclonal Antibody. Detects K40 acetylation of alpha-tubulin; signal specifically increased by modification with tubulin acetyl transferase alpha-TAT1. Isotype: Mouse IgG1. Clone: TEU318. Applications: ICC, WB. Liquid. In PBS containing 10% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide. Microtubules are key elements of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton that dynamically assemble from heterodimers of alpha- and beta-tubulin. Two different mechanisms can generate microtubule diversity: the expression of different alpha- and beta-tubulin genes, referred to as tubulin isotypes, and the generation of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) on alpha- and beta-tubulin. Tubulin PTMs include the well-known acetylation or phosphorylation, and others that have so far mostly been found on tubulin, detyrosination/tyrosination, polyglutamylation and polyglycylation. These PTMs might have evolved to specifically regulate tubulin and microtubule functions. Tubulin acetylation was discovered on K40 of flagellar alpha-tubulin in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and is generally enriched on stable microtubules in cells. It is located on the microtubule lumenal surface. As a result of its localization at the inner face of microtubules, K40 acetylation might rather affect the binding of microtubule inner proteins, a poorly characterized family of proteins. Functional experiments in cells have further suggested that K40 acetylation regulates intracellular transport by regulating the traffic of kinesin motors probably by indirect mechanisms. Acetyltransferase alpha-Tat1 (or Mec-17) specifically acetylate alpha-tubulin K40. Acetylation of tubulin by alpha-Tat1 accumulates selectively in stable, long-lived microtubules thus explaining the link between this posttranslational modication and stable microtubules in cells. However, the direct cellular function of K40 acetylation on microtubules is still unclear.
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Product Description:
Microtubules are key elements of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton that dynamically assemble from heterodimers of alpha- and beta-tubulin. Two different mechanisms can generate microtubule diversity: the expression of different alpha- and beta-tubulin genes, referred to as tubulin isotypes, and the generation of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) on alpha- and beta-tubulin. Tubulin PTMs include the well-known acetylation or phosphorylation, and others that have so far mostly been found on tubulin, detyrosination/tyrosination, polyglutamylation and polyglycylation. These PTMs might have evolved to specifically regulate tubulin and microtubule functions. Tubulin acetylation was discovered on K40 of flagellar alpha-tubulin in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and is generally enriched on stable microtubules in cells. It is located on the microtubule lumenal surface. As a result of its localization at the inner face of microtubules, K40 acetylation might rather affect the binding of microtubule inner proteins, a poorly characterized family of proteins. Functional experiments in cells have further suggested that K40 acetylation regulates intracellular transport by regulating the traffic of kinesin motors probably by indirect mechanisms. Acetyltransferase alpha-Tat1 (or Mec-17) specifically acetylate alpha-tubulin K40. Acetylation of tubulin by alpha-Tat1 accumulates selectively in stable, long-lived microtubules thus explaining the link between this posttranslational modication and stable microtubules in cells. However, the direct cellular function of K40 acetylation on microtubules is still unclear.
Purity:
>95% (SDS-PAGE)
Source / Host:
Purified from concentrated hybridoma tissue culture supernatant.
Specificity:
Detects K40 acetylation of alpha-tubulin; signal specifically increased by modification with tubulin acetyl transferase alpha-TAT1.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Primary Antibodies
UNSPSC Number:
12352203
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
Isolation and characterization of libraries of monoclonal antibodies directed against various forms of tubulin in Paramecium: A.M. Callen, et al.; Biol. Cell 81, 95 (1994) | Where and when is microtubule diversity generated in Paramecium? Immunological properties of microtubular networks in the interphase and dividing cells: A. Fleury, et al.; Protoplasma 189, 37 (1995) | Structural inheritance in Paramecium: ultrastructural evidence for basal body and associated rootlets polarity transmission through binary fission: F. Iftode & A. Fleury-Aubusson; Biol. Cell 95, 39 (2003) | Investigating tubulin posttranslational modifications with specific antibodies: M.M. Magiera & C. Janke; In Methods Cell Biol. (Burlington: Academic Press) 115, 247 (2013)