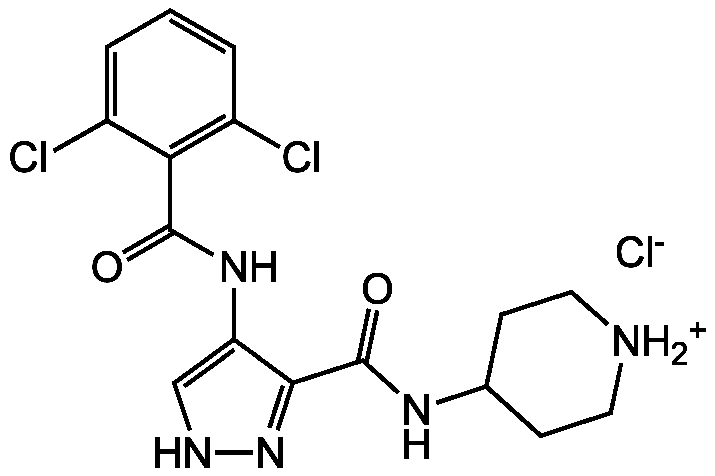
AT7519 hydrochloride
Product Code:
SYN-1010
SYN-1010
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
-20°C
-20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| SYN-1010-M100 | 100 mg | Enquire |
Quantity:
| SYN-1010-M001 | 1 mg | £80.00 |
Quantity:
| SYN-1010-M005 | 5 mg | £127.00 |
Quantity:
| SYN-1010-M010 | 10 mg | £186.00 |
Quantity:
| SYN-1010-M050 | 50 mg | £643.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
AT-7519
Appearance:
Solid.
CAS:
902135-91-5
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
InChi:
InChI=1S/C16H17Cl2N5O2.ClH/c17-10-2-1-3-11(18)13(10)15(24)22-12-8-20-23-14(12)16(25)21-9-4-6-19-7-5-9;/h1-3,8-9,19H,4-7H2,(H,20,23)(H,21,25)(H,22,24);1H
InChiKey:
PAOFPNGYBWGKCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 902135-91-5. Formula: C16H17Cl2N5O2 . HCl. MW: 382.2 . 36.5. AT7519 is a potent inhibitor of several CDK family members. AT7519 showed potent antiproliferative activity (40-940nM) in a panel of human tumor cell lines, and the mechanism of action was shown here to be consistent with the inhibition of CDK1 and CDK2 in solid tumor cell lines. AT7519 caused cell cycle arrest followed by apoptosis in human tumor cells and inhibited tumor growth in human tumor xenograft models. Tumor regression was observed following twice daily dosing of AT7519 in the HCT116 and HT29 colon cancer xenograft models. Also it has been shown that the biological effects are linked to inhibition of CDKs in vivo and that AT7519 induces tumor cell apoptosis in these xenograft models. Moreover, AT7519 has an attractive biological profile and is well tolerated and effective making it a more plausible candidate for clinical development than previously available CDK inhibitors. In in vitro kinase assays AT7519 showed nanomolar levels of activity from <10 to 2400 for cyclins; only one other non-cyclin related kinase was inhibited at levels below 10µM (GSK3beta, 89nM), all others tested had IC(50)'s of greater than 10,000nM.
Molecular Formula:
C16H17Cl2N5O2 . HCl
Molecular Weight:
382.2 . 36.5
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Product Description:
AT7519 is a potent inhibitor of several CDK family members. AT7519 showed potent antiproliferative activity (40-940nM) in a panel of human tumor cell lines, and the mechanism of action was shown here to be consistent with the inhibition of CDK1 and CDK2 in solid tumor cell lines. AT7519 caused cell cycle arrest followed by apoptosis in human tumor cells and inhibited tumor growth in human tumor xenograft models. Tumor regression was observed following twice daily dosing of AT7519 in the HCT116 and HT29 colon cancer xenograft models. Also it has been shown that the biological effects are linked to inhibition of CDKs in vivo and that AT7519 induces tumor cell apoptosis in these xenograft models. Moreover, AT7519 has an attractive biological profile and is well tolerated and effective making it a more plausible candidate for clinical development than previously available CDK inhibitors. In in vitro kinase assays AT7519 showed nanomolar levels of activity from < 10 to 2400 for cyclins; only one other non-cyclin related kinase was inhibited at levels below 10µM (GSK3beta, 89nM), all others tested had IC(50)'s of greater than 10,000nM.
Purity:
>95%
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO or ethanol.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Protein Kinase Modulators
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
Biological characterization of AT7519, a small-molecule inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases, in human tumor cell lines: M.S. Squires, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 8, 324 (2009)