ProSci works with Dr. Sadayappan to create a set of custom antibodies used to study cardiomyopathy.
Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein-C (cMyBP-C) is a protein present in cardiac muscle that has been shown to affect the organizational structure of the muscle itself by forming a link between the thin and thick filaments of the sarcomere, which implicates cMyBP-C as a regulator of rate and force of contraction in mammalian myocardium. Dr. Sadayappan, an associate professor and researcher at Loyola University Chicago, is dedicated to investigating and determining the structure, regulation and function of cMyBP-C in cardiac and skeletal tissue. In part, this interest stems from cMyBP-C’s role in cardiomyopathy. Familial hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathies have been closely associated with mutations in the cMyBP-C gene, accounting for approximately 40% of all mutations that have been linked to cardiomyopathies.
Cardiac myosin binding protein-C: The cardiac-specific regions (C0 and M domain, as well as an insert in the C5 domain) are marked in light green. A proline-alanine (P/A)-rich region and A-band localization regions are shown.
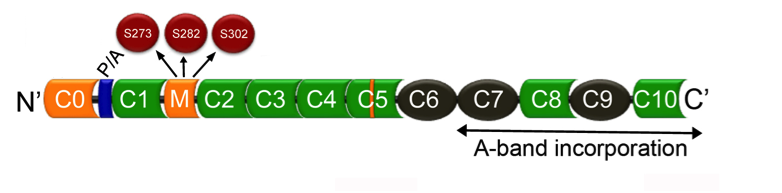
Compared to the skeletal forms of MyBP-C, cMyBP-C has unique multiple phosphorylation sites within the M-domain (Figure), such as Ser-273, Ser-282 and Ser-302 (Mouse, Uniprot ID 070468). The multiple phosphorylation sites are targeted by protein kinase A, protein kinase C, CaMKII, protein kinase D, and ribosomal s6 kinase, affecting sarcomere structure and function. Furthermore, GSKβ3 phosphorylates cMyBP-C at Ser-133, which is positioned in the proline-alanine rich region. cMyBP-C undergoes other post-translational modifications, such as acetylation, glutathionylation, citrullination and O-GlcNAcylation, suggesting that cMyBP-C is a central downstream target of signaling in the sarcomere. cMyBP-C serves as a crucial junction for complex signaling events in the regulation of cardioprotection and cardiac contractility. As such, cMyBP-C undergoes many post-translational modifications, some of which alter cMyBP-C proteolysis during muscle injury. The link between cMyBP-C modification, mutation, and pathogenesis has yet to be deciphered but is a focus of Dr. Sadayappan’s research. Through ProSci, Dr. Sadayappan has developed several pan and phoshpho-serine specific antibodies against cMyBP-C that have been instrumental in the study of cMyBP-C and its role in cardiomyopathy, resulting in several publications.
Find out how ProSci can help your Antibody needs today!
