CD1d, non-classical MHC molecules, present phospholipid & glycosphingolipid antigens to iNKT cells. MBL tetramers help measure CD1d positive NKT cells
Protective Role of Invariant Natural Killer T (iNKT) cells
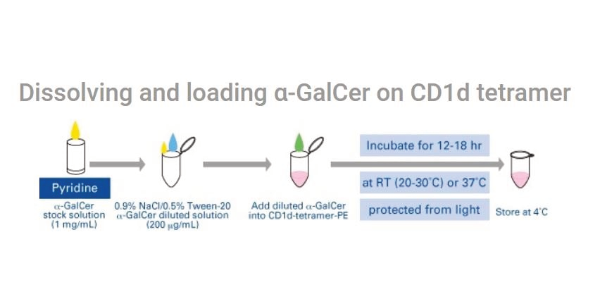

CD1d, non-classical MHC molecules, present phospholipid & glycosphingolipid antigens to iNKT cells. MBL tetramers help measure CD1d positive NKT cells
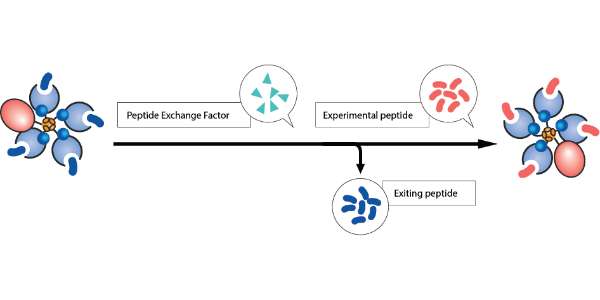
Here are the highlights of some of the influential publications that have utilised MBLI QuickSwitch™ Tetramer Kits in 2023.

RSV is a significant respiratory virus in young children, & is the primary cause of hospitalisations, particularly bronchiolitis & pneumonia.
There is more data that highlights the significant role of m7G modification in human diseases, particularly cancer.
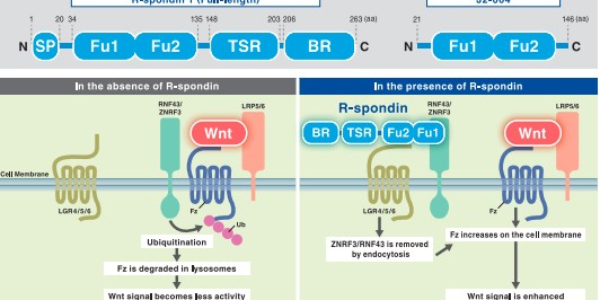
MBL have a new innovative product available: Human R-spondin 1, for use in organoid culture.
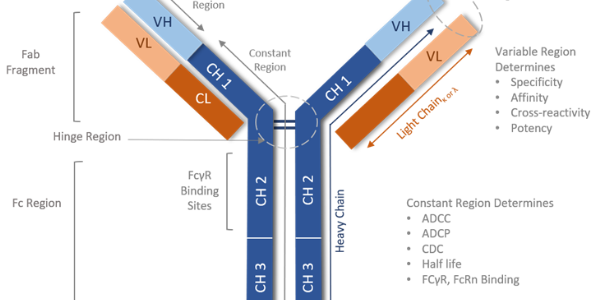
In vivo antibody studies offer a wide range of applications. Discover the significant impact of antibody selection on your experiment.
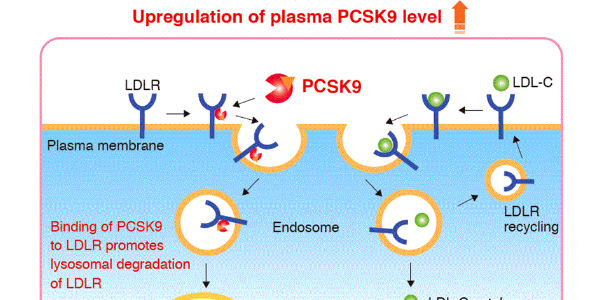
MBL International is at the forefront of providing PCSK9 assay kits and reagents to support the advancement of PCSK9 studies.
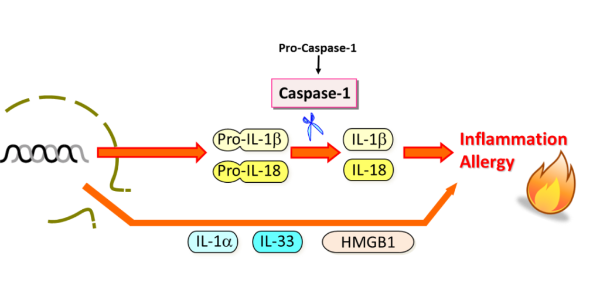
Researchers take advantage of MBL International’s recombinant IL-18 to activate varying cells like peripheral blood cells, macrophages, NK cells and T cells to identify targets.

Wang, Wenfeng, et al 2023, selected the top 15 top peptides for self-antigen for their study. By using the QuickSwitch™ kit, they successfully switched 6 peptides to the tetramer complex with an efficiency of over 75%.
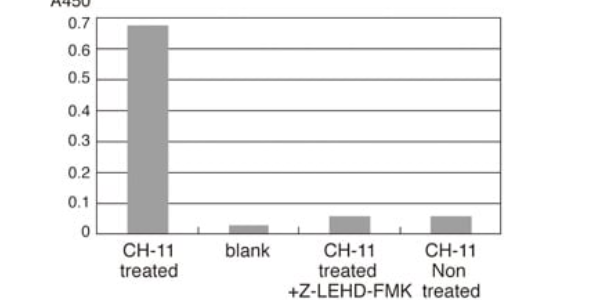
MBLI ‘s APOPCYTO Caspase-3,8,9 Colorimetric Assay Kit detects caspase activity in cell extract with LEHD-pNA as a substrate, in which LEHD sequence is recognised by each active caspase selectively.