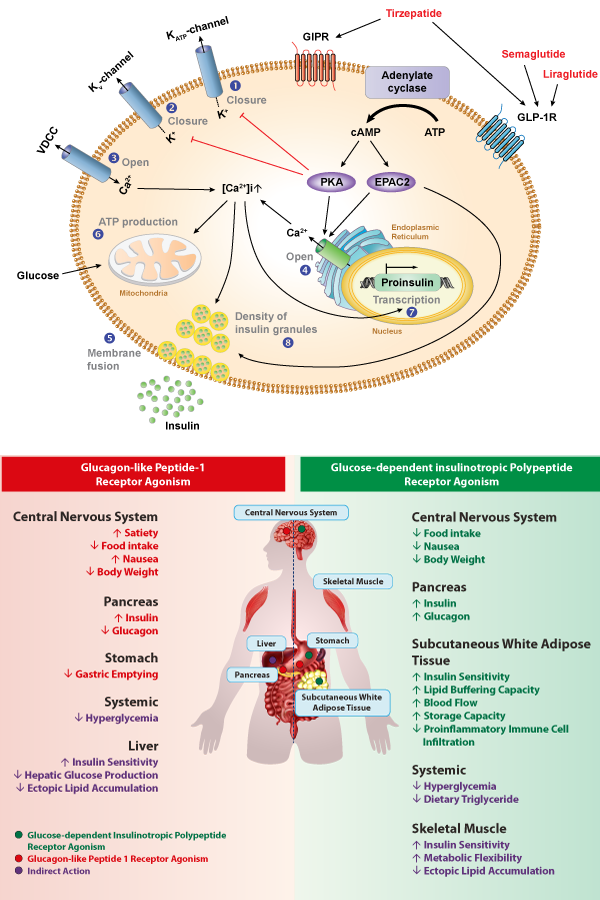
GIP (Gastric inhibitory polypeptide; Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) and GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide-1) are the two primary incretin hormones secreted from the intestine on ingestion of glucose or nutrients to stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells. GIP and GLP-1 exert their effects by binding to their specific receptors, the GIP receptor (GIPR) and the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R), which belong to the G-protein coupled receptor family. Receptor binding activates and increases the level of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate in pancreatic β cells, thereby stimulating insulin secretion glucose-dependently. In addition to their insulinotropic effects, GIP and GLP-1 play critical roles in various biological processes in different tissues and organs that express GIPR and GLP-1R, including the pancreas, fat, bone and the brain. Within the pancreas, GIP and GLP-1 together promote β cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis, thereby expanding pancreatic β cell mass, while GIP enhances postprandial glucagon response and GLP-1 suppresses it. In adipose tissues, GIP but not GLP-1 facilitates fat deposition. In bone, GIP promotes bone formation while GLP-1 inhibits bone absorption. In the brain, both GIP and GLP-1 are thought to be involved in memory formation as well as the control of appetite.
Therefore, in addition to their effects on insulin secretion, GLP-1 and GIP also have other metabolic effects, such as reducing glucagon secretion from the pancreas, slowing down gastric emptying and promoting satiety.
GLP-1R agonists work by mimicking the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). By activating GLP-1 receptors, GLP-1R agonists help to increase insulin release and lower blood sugar levels. They also slow down the emptying of food from the stomach, which can help to reduce post-meal spikes in blood sugar.
GIPR agonists work by targeting the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor. By activating GIP receptors, GIP agonists can enhance insulin secretion and lower blood sugar levels. They may also reduce appetite and food intake, which can help to support weight loss.
Literature References:
- How May GIP Enhance the Therapeutic Efficacy of GLP-1? R.J. Samms, et al.; Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 31, 410 (2020) (Review)
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects: X. Zhao, et al.; Front. Endocrinol. 12, 721135 (2021) (Review)
- GLP-1 and GIP receptor signaling in beta cells – A review of receptor interactions and co-stimulation: A. Mayendraray, et al.; Peptides 151, 170749 (2022) (Review)
- Bumps and humps in the success of Tirzepatide as the first GLP1 and GIP receptor agonist: R. Ali, et al.; Health Sci. Rev. 4, 100032 (2022) (Review)
- GLP-1a: Going beyond Traditional Use: L. Fornari Laurindo, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 739 (2022) (Review)
- Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP‑1 receptor co‑agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with unmatched effectiveness regarding glycaemic control and body weight reduction: M.A. Nauck & D.A. D’Alessio; Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 21, 169 (2022) (Review)
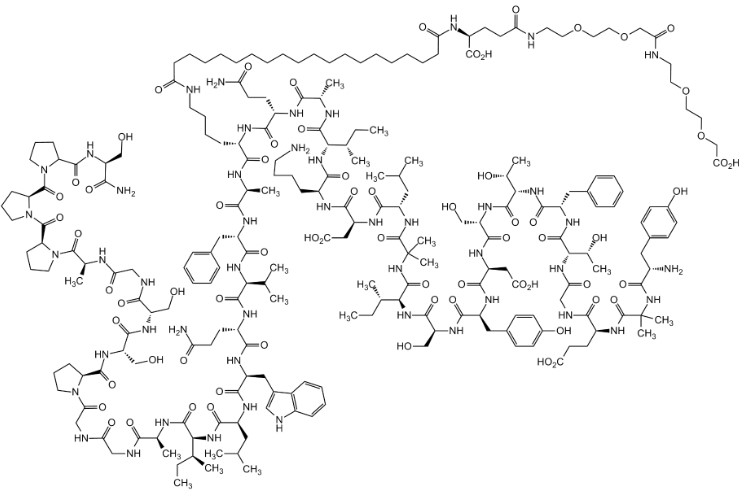
Tirzepatide
Sequence: H-Tyr-{Aib}-Glu-Gly-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Asp-Tyr-Ser-Ile-{Aib}-Leu-Asp-Lys-Ile-Ala-Gln-{diacid-γ-Glu-(AEEA)2-Lys}-Ala-Phe-Val-Gln-Trp-Leu-Ile-Ala-Gly-Gly-Pro-Ser-Ser-Gly-Ala-Pro-Pro-Pro-Ser-NH2
Tirzepatide is a novel dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. Tirzepatide potently activates the GLP-1R signalling pathway to stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion through activity at the GIP receptor (GIPR) or the GLP-1R. Tirzepatide has glucose-lowering effects. It is an antidiabetic agent against type 2 diabetes (T2D), stimulating insulin and suppressing glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. Tirzepatide was also shown to delay gastric emptying, lower fasting and postprandial glucose concentration, decrease food intake and reduce body weight in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Product Information:
CAS: 2023788-19-2
Formula: C225H348N48O68
MW: 4813.5
Originally posted on adipogen.com/glp-1-gip-receptor-agonists
Caltag Medsystems is the distributor of Adipogen products in the UK and Ireland. If you have any questions about these products, please contact us.
