MEGA-8 (ultrapure)
Product Code:
AG-CC1-0007
AG-CC1-0007
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
+20°C
+20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CC1-0007-G001 | 1 g | £101.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CC1-0007-G005 | 5 g | £371.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges to UK mainland customers, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
N-Octanoyl-N-methylglucamine; OMEGA
Appearance:
White crystalline powder.
CAS:
85316-98-9
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from moisture.
InChi:
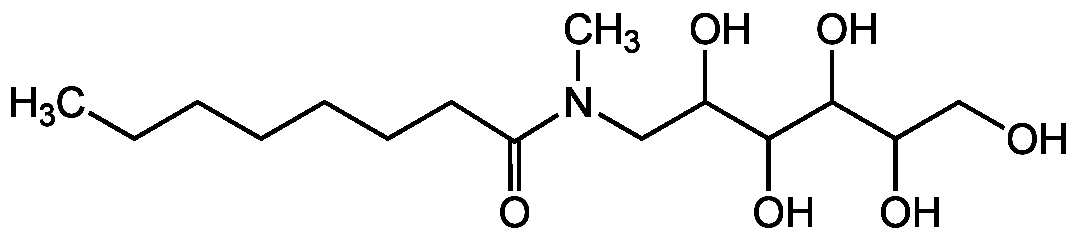
InChI=1S/C15H31NO6/c1-3-4-5-6-7-8-13(20)16(2)9-11(18)14(21)15(22)12(19)10-17/h11-12,14-15,17-19,21-22H,3-10H2,1-2H3
InChiKey:
SBWGZAXBCCNRTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 85316-98-9. Formula: C15H31NO6. MW: 321.4. Non-ionic water-soluble detergent with nondenaturing properties. Transparent in the UV region. Relatively high critical micelle concentration (CMC) value (79mM/l). Ideal for studying the conformation and function of proteins, keeping the secondary and tertiary structure intact, therefore suited for solubilizing membrane proteins without altering biological activity. Efficiently separates hydrophilic proteins from membrane spanning, hydrophobic proteins. Ideal for use as membrane protein solubilizer.
MDL:
MFCD00134152
Molecular Formula:
C15H31NO6
Molecular Weight:
321.4
Other data:
The phospholipid bilayer is the basic structure of the cell membrane. In membrane biochemistry research, membrane proteins are solubilized and purified to study their structure and function. Proteins bound to cell membranes have hydrophobic sites buried within the phospholipid bilayers and hydrophilic sites facing toward the water layer. Detergents are used to isolate large insoluble molecules such as proteins. Detergents interact with the hydrophobic sites of proteins, which are then solubilized in the water layer, thus separating membrane proteins. It is important to choose a detergent that does not disrupt the bioactivities of target proteins. A detergent requires the following characteristics to be suitable for isolation of membrane proteins: Sufficient protein solubilization capability. | No denaturing or inactivation of proteins. | No interference with protein activities. | No precipitation at 4°C. | Appropriate critical micelle concentrations (CMC) and micelle size. | No absorption in the UV region. | No toxicity. | Availability of detergent detection methods. | Non-ionic detergent if ion exchange chromatography is used.
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Non-ionic water-soluble detergent with nondenaturing properties. Transparent in the UV region. Relatively high critical micelle concentration (CMC) value (79mM/l). Ideal for studying the conformation and function of proteins, keeping the secondary and tertiary structure intact, therefore suited for solubilizing membrane proteins without altering biological activity. Efficiently separates hydrophilic proteins from membrane spanning, hydrophobic proteins. Ideal for use as membrane protein solubilizer.
Purity:
>99% (HPLC)
SMILES:
CCCCCCCC(=O)N(C)CC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)CO
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water (>2g/10ml at 20°C).
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
The structures of 1-deoxy-(N-methyloctanamido)-D-glucitol (MEGA-8) and 1-deoxy-(N-methylundecanamido)-D-glucitol (MEGA-11): G.A. Jeffrey & H. Maluszynska; Acta Crystallogr. B 45, 447 (1989) | Solubility properties of the alkylmethylglucamide surfactants: A. Walter, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1029, 67 (1990) | Differential solubilization of lipids along with membrane proteins by different classes of detergents: P. Banerjee, et al.; Chem. Phys. Lipids 77, 65 (1995) | Salt Effect on Critical Micelle Concentrations of Nonionic Surfactants, N-Acyl-N-methylglucamides (MEGA-n): S. Miyagishi, et al.; J. Colloid Interface Sci. 238, 91 (2001) | Blending effects on adsorption and micellization of different membrane protein solubilizers: a thermodynamic study on three mixed systems of CHAPS with MEGA-8, -9 and -10 in pH 7.2 phosphate buffer solution: J.S. Ko, et al.; Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 45, 90 (2005)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-Dodecyl-beta-D-maltoside (high purity) | AG-CC1-0004 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n-Octyl-beta-D-thioglucopyranoside (high purity) | AG-CC1-0005 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n-Dodecyl-alpha-D-maltoside (high purity) | AG-CC1-0006 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||