How do you quantify newly synthesised RNA? There are several ways to detect synthesised RNA, but these methods have their complications. The 5-Bromouridine immunoprecipitation chase (BRIC) Kit offers the the most suitable method for RNA decay analysis.
Regulation of gene expression by RNA degradation is a critical step for the coordination of many physiological processes. Decay pathways also play important roles in mRNA surveillance systems. Traditionally, transcriptional inhibitors such as Actinomycin D have been widely used to analyse RNA degradation. However, these methods have been shown to influence cellular physiology, including splicing, polyadenylation and other post transcriptional events.
Recently, uridine analogues have been used to for genome-wide RNA decay analysis in mammalian cells, without the need for transcriptional inhibitors. By incorporating uridine analogues into RNA such as BrU (5-Bromouridine), EU (5-Ethynyl Uridine) and 4sU (4-Thiouridine), labelled RNA can be isolated by immunoprecipitation to study the stability and half-life of different RNAs.
EU (5-Ethynyl Uridine) labelling methods require biotinylation of the labelled RNA to specifically collect the biotin-labelled RNA by streptavidin beads. This biotinylation step can be a trigger for RNA degradation, skewing the apparent stability of RNA. 4sU (4-Thiouridine) permits base pairing with guanine instead of adenine, which causes base changes in the RNA sequence.
BrU (5-Bromouridine) is less toxic to cells than other uridine modifications and can be easily immunoprecipitated by the antibromodeoxyuridine (BruD) antibody through its cross reactivity. Unlike EU and 4sU based analysis, the 5-Bromouridine immunoprecipitation chase (BRIC) method avoids the mentioned undesirable effects for downstream applications such as RT-qPCR, deep sequencing, or microarray, making it the most suitable method for RNA decay analysis.
How can MBLI help? Anti-BrdU antibody and BRIC Kit available
MBL International offers an anti-BrdU antibody that has cross reactivity with BrU. Using this antibody, they have developed a comprehensive 5-bromouridine immunoprecipitation chase (BRIC) kit to detect RNA synthesis.
- Low toxicity
- Avoid undesirable effects of alternative uridine analogues
- Immunoprecipitation of labelled RNA for downstream analysis.
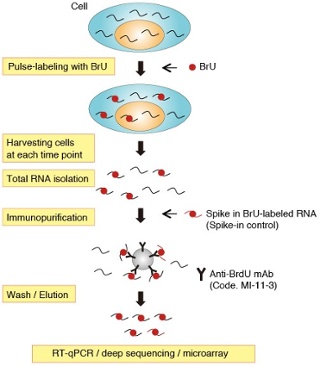
The BRIC Kit enables determination of RNA stability by chasing chronological decreases of BrU-labelled RNA under physiologically undisturbed conditions. Cells are pulse labelled with BrU and harvested at set time points, then BrU-labelled RNA is specifically immunoprecipitated with the anti-BrdU antibody. The resulting immunocomplex can then be isolated using protein G magnetic beads.
BrU-labelled RNA can then be analysed by downstream techniques such as RT-qPCR, deep sequencing, or microarray to profile the stability and half-life of the RNA.
Applications
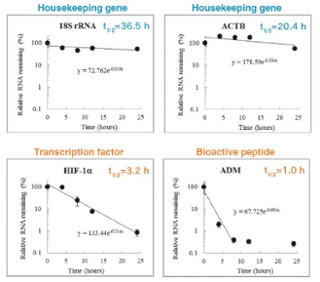
The RNA half-life of housekeeping genes tends to be longer than regulatory genes such as cell cycle regulators, cytokines, transcription factors and oncoproteins. Classification of RNAs by half-life may contribute to discover novel RNA biomarkers and targets of drugs. BRIC kit is a powerful tool for RNA metabolism analysis.
Available Products
The following are RNA-immunoprecipitation based kits that utilise MBLI’s anti-BrdU antibody and will further help your RNA research:
BRIC Kit: BRIC Kit
RiboTrap Kit: RiboTrap
Anti-BrdU mAb: MI-11-3
References
- Tani, H., et al., genome Res. 22, 947-956 (2012
- Tani, H. and Akimitsu, N., RNA Biol. 9, 1233-1238 (2012)
- Imamachi, N., , et al., Methods 67, 55-63 (2014)
- Tani, H., et al., PLoS One 8, e55684 (2013)
- Tani, H., et al., RNA Biol. 9, 1233-1238 (2012)
