CD1d molecules are non-classical MHC molecules that present phospholipid and glycosphingolipid antigens to invariant Natural Killer T (iNKT) cells. These cell types are involved in the regulation of nearly all aspects of innate and acquired immune responses. Due to CD1d involvement in multiple aspects of the immune response, iNKT cells are being researched widely for their role and therapeutic potential in many diseases; for example schistosomiasis, glioblastoma, multiple myeloma, systemic lupus erythematosus and viral infections.
Recently, Sada, Masashi, et al. (2023) investigated whether the activation of iNKT cells by α-galactosylceramide (αGC), a specific activator for iNKT cells, could attenuate DOX-induced cardiomyocyte death and cardiomyopathy. Given that the activation of iNKT cells has a beneficial impact on cardiac remodelling following post-myocardial infarction and ischemia-reperfusion injury, in the present study, αGC-loaded murine CD1d tetramer (TS-MCG-1) was used to examine cardiac mononuclear cells from 8 different mice groups. The data indicated that the activation of iNKT cells attenuates DOX-induced cardiac dysfunction (1). Overall, the study showed a protective mechanism against DOX-induced cardiomyopathy through the activation of iNKT cells (1).
Invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells are unique immune cells that link innate and adaptive immunity and have recently been discovered to play a significant role in immunological response and immune regulation (2). Li, Zhao, et al. (2023) wanted to understand the impact of adoptive infusion in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). To gain better insights into the effects of adoptive therapy of iNKT cells with a specific phenotype and function in RA mice. After intraperitoneal injection of α-GalCer into 100 DBA/1 mice, the detection of iNKT was observed by PE-α-GalCer-CD1d Tetramer (TS-MCG-1) in the thymus and spleen of mice in each group. The iNKT frequency of the cell treatment group was significantly higher than that of the α-GalCer group after treatment (2). In summary, adoptive therapy with iNKT cells in RA mice may correct the imbalance of iNKT subsets in the thymus of RA mice in turn providing a treatment of RA targeting iNKT cells (2).
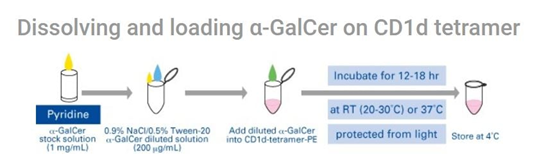
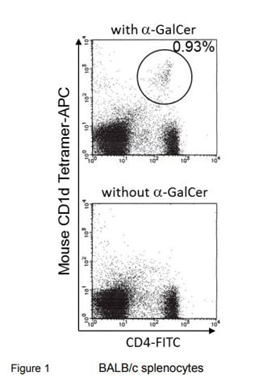
The research highlights (1, 2) demonstrate how MBL’s technology permits accurate measurement of CD1d-positive NKT cells. These tetramers are prepared by tetramerisation of complexes of CD1d and β2m by PE- or APC-labelled streptavidin. Binding this reagent to α-GalCer enables highly sensitive detection of CD1d-restricted NKT cells and can be combined with antibodies to study NKT cell function through flow cytometry.
| Product Code | Product Name |
| TS-MCD-1 | Mouse CD1d Tetramer-SA |
| TS-MCG-1 | Mouse CD1d Tetramer (α-GalCer loaded) |
| TS-HCD-1 | Human CD1d Tetramer |
| TS-HCG-1 | Human CD1d Tetramer (α-GalCer loaded) |
References:
- Sada, Masashi, et al. “IFN-γ-STAT1-ERK Pathway Mediates Protective Effects of Invariant Natural Killer T Cells Against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Death.” JACC: Basic to Translational Science (2023).
- Li, Zhao, et al. “Epigenetic regulation of iNKT2 cell adoptive therapy on the imbalance of iNKT cell subsets in thymus of RA mice.” Cellular Immunology 386 (2023): 104703.
Information provided by MBL.
Caltag Medsystems is the distributor of MBL products in the UK and Ireland. If you have any questions about these products, please contact us.
