The HITAlert Kit™ is a CE/IVD functional assay for the diagnosis of Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia. This kit uses donor platelets (PRP) which are incubated in the presence of patient serum and in the presence or absence of heparin. A platelet activation marker is used to identify and quantitate the activated platelets caused by pathogenic antibodies, which can be visualised using flow cytometry. As a result, the HITAlert™ kit is a highly specific assay that can detect other pathogenic antibodies produced from multiple heparin complexes (including IL-8 and NAP-2) in a rapid and simple method.
Special Features of The HITAlert Kit™:
– Complete kit with ready-to-use components
– Non-radioactive method
– Rapid results (<2 hr)
– CE/IVD for the diagnosis of Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia.
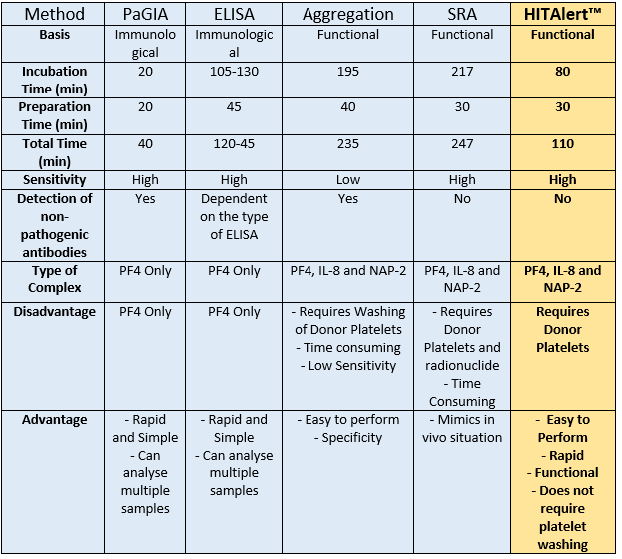
For detection of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT), two different types of assays can be used; Immunological Assays and Functional Assays. Functional Assays such as the Serotonin-release assay (SRA), whilst sensitive and specific, are non-feasible because of the use of radio isotypes. Other functional assays, e.g Aggregation Assays are more time consuming and have a low sensitivity for detection of pathogenic antibodies. Meanwhile, immunological assays such as ELISAs and PaGIA (gel immunoassay) method can produce false negative results of over 10%, and a 20% disagreement against the results from the more sensitive SRA assay.
Comparison of The HITAlert Kit™ amongst other methods for detecting Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia:
HITAlert Kit™ Components (sufficient to test 6 patients – 30 tests):
– Assay Buffer (5m)
– Heparin (150µl)
– Platelet Activator (Ca-Ionophore) – 1 Vial
– Staining Buffer (20ml)
– Platelet Marker (monoclonal antibody) (200µl)
– Platelet Activation Marker (Recombinant Protein) (200µl)
– Heparin 1000 U/ml (150 µl)
– 2.2ml PP Vials used for the sample incubation
Product Information:
Product Name: HITAlert Kit
Product Code: IQP-396
Size: 25 Test
Caltag Medsystems is the distributor of IQ Products products in the UK and Ireland. If you have any questions about these products, please contact us.
References:
Warkentin TE, Heddle NM (2003). Laboratory Diagnosis of Immune Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia. Current Hematology Reports 2: 148-157.
Tomer, A (1997). A sensitive and specific functional flow cytometric assay for the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. British Journal of Haematology 98(3): 648- 56.
Tomer A, Masalunga C, and Abshire TC (1999). Determination of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a rapid flow cytometric assay for direct demonstration of antibody mediated platelet activation. American Journal of Hematology 61(1): 53-61.
Greinacher A, Juhl D, Strobel U, Wessel A, Lubenow N, Selleng K, Eichler P, and Warkentin TE (2007). Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a prospective study on the incidence, platelet-activating capacity and clinical significance of antiplatelet factor 4/heparin antibodies of the IgG, IgM, and IgA classes. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 5; 1666.
Tomer A (1997). Sensitivity and specificity of laboratory tests for the diagnosis of heparin- induced thrombocytopenia. Laboratory Hematology 3:174-5.
Warkentin TE, Sheppard JI, Raschke R, and Greinacher A (2007). Performance characteristics of a rapid assay for antiPF4/heparin antibodies: the particle immunofiltration assay. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 5: 2308–10.