The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) and the autophagic-lysosomal pathway are the two major degradation systems for both native and misfolded proteins in eukaryotic cells. They do not act independently from each other. Defective autophagy results in the accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins, impacting the flux of the UPS, while dysfunction of the UPS can promote a compensatory induction of autophagy. Through protein degradation and the maintenance of protein homeostasis, the UPS regulates many normal cellular processes including signal transduction, cell cycle control, transcription and apoptosis (see Figure). The regulated proteolysis of bulk and misfolded proteins is strictly controlled by the 26S proteasome complex.
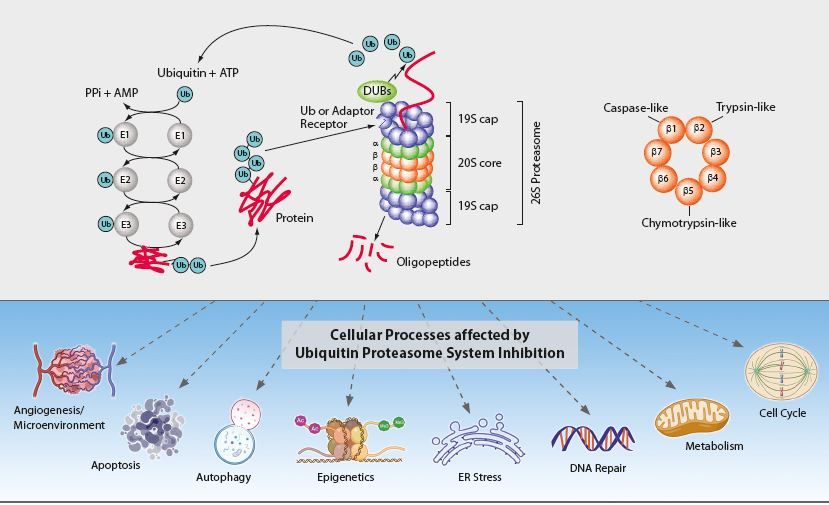
The 26S proteasome complex recognises polyubiquitinated proteins, which were marked for elimination by the E1, E2 and E3 ubiquitinating enzymes (see Figure). Upon recognition, unfolding and transfer of the de-ubiquitinated target protein by the 19S regulatory cap into the interior of the cylindrical 20S proteasome core particle, protein degradation is facilitated by catalytic β-subunits having nucleophilic N-terminal threonine (Thr1) residues. Although eukaryotic 20S proteasomes harbour seven different β-subunits in their two-fold symmetrical α7β7β7α7 stacked complexes, only three β-subunits per β-ring [subunits β1 (caspase-like), β2 (trypsin-like) and β5 (chymotrypsin-like)] are proteolytically active. These three β-subunits are major targets for small-molecule proteasome inhibitors. Proteasome inhibition has implications in a number of human diseases such as cancer (e.g. multiple myeloma (MM)), inflammation and ischemic stroke and is an important therapeutic target.
Several components of the UPS have been validated as potential anticancer targets, including 20S proteasomes, 19S proteasome-associated deubiquitinases (DUBs) and ubiquitin ligases (E3s). One of the strategies to improve the current status of cancer treatment is to repurpose old drugs with UPS-inhibitory properties as new anticancer agents.
Caltag Medsystems provide a variety of Ubiquitin & Proteasome Research Reagents on behalf of AdipoGen Life Sciences:
1. Standard Proteasome Inhibitors
2. Other Proteasome Inhibitors/Modulators
3. Fluorescent Substrates for Ubiquitin-Proteasome Activity Measurement
4. Proteasome Complex Modulators
5. SUMO-Related Inhibitors
MLN4924 [NAE Inhibitor] Solution
6. Proteasome Assay Kits & 20S Proteasome/20S Immunoproteasome Complexes
The two proteasome kits are designed to test for specific activity of 20S immunoproteasome or 20S constitutive proteasome, and include purified proteasomes, AMC-conjugated substrates, specific inhibitors and necessary buffers and solutions. Fluorescence detection can be performed at Excitation/Emission (nm): 345/445, allowing for a real-time readout of specific activity.
All highly active and pure proteasomes offered by AdipoGen Life Sciences are able to proteolytically degrade substrates in an ATP-independent manner.
20S Immunoproteasome Assay Kit
20S Constitutive Proteasome Assay Kit
20S Immunoproteasome (human) (untagged)
20S Immunoproteasome (mouse) (untagged)
20S Immunoproteasome (rat) (untagged)
20S Proteasome (human) (untagged)
20S Proteasome (mouse) (untagged)
20S Proteasome (rat) (untagged)
Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (Europium-Cryptate)
Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (Cy5)
Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (6-FAM)
7. Specialty Degradation Reagents
D-Biotin p-nitrophenyl ester (Biotin-ONP; BNP)
Lipoyl-TRIM21 (human) (rec.) (His)
8. Buffers and Solutions
Originally posted on adipogen.com/ubiquitin-proteasome-system
Caltag Medsystems is the distributor of Adipogen products in the UK and Ireland. If you have any questions about these products, please contact us.
