Full-thickness skin grafts (FTSGs) are commonly used in surgeries like hernia repairs, but how they integrate and heal long-term is still not fully understood. A recent study focused on extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling and the role of fibroblasts in skin graft healing. Using collagen hybridising peptide (CHP) staining, researchers observed active collagen turnover in grafts, indicating that the ECM was being actively remodelled.
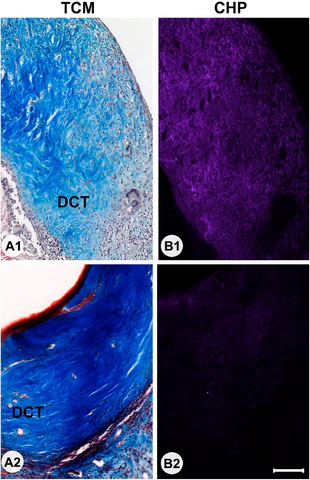
The study found that S100A4-positive fibroblasts were linked to areas with high CHP staining, suggesting these cells play a critical role in collagen degradation and remodelling. Grafts with high CHP density had immature collagen, showing that active remodelling was still happening, while grafts with low CHP staining had more mature collagen, indicating they were in a later stage of healing.
These findings emphasise the importance of ECM remodeling in successful graft integration and highlight potential markers to monitor skin graft healing. Ultimately, this research could lead to improved monitoring and treatment strategies for better skin graft outcomes.
References: Tjust, Anton Erik et al. “Evaluation of Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Full-thickness Skin Grafts in Mice.” The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry: official journal of the Histochemistry Society vol. 72,2 (2024): 79-94. doi:10.1369/00221554231225995
Information originally posted on: https://www.3helix.com/blogs/news/understanding-ecm-remodeling-in-full-thickness-skin-grafts-insights-from-collagen-hybridizing-peptide-staining?currency=USD
Caltag Medsystems is the distributor of 3Helix products in the UK and Ireland. If you have any questions about these products, please contact us.
