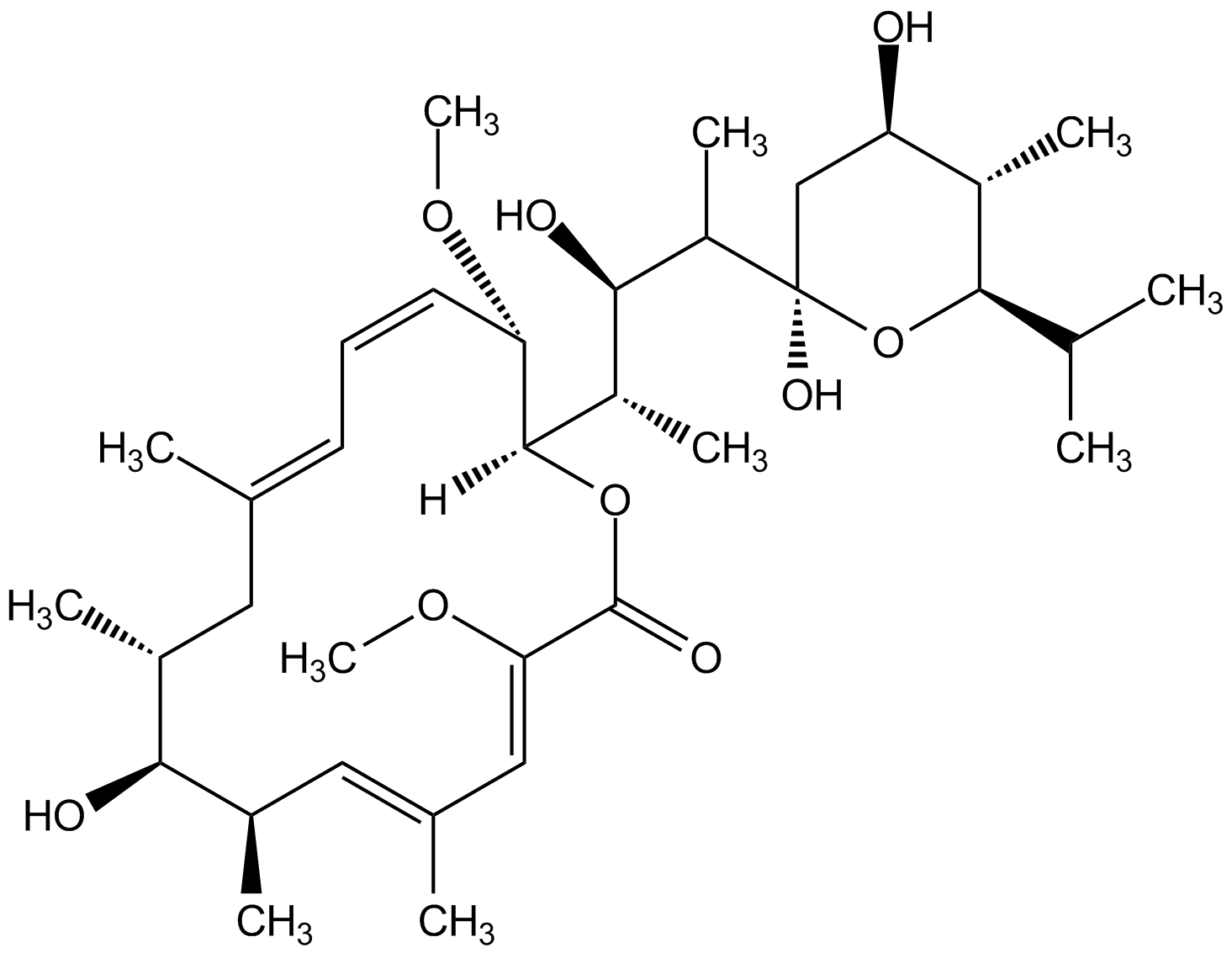
Bafilomycin A1 (high purity)
Product Code:
AG-CN2-2001
AG-CN2-2001
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-2001-C100 | 100 ug | £105.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-2001-M001 | 1 mg | £190.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-2001-M005 | 5 mg | £640.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
NSC381866; BafA1
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
88899-55-2
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep under inert gas. Protect from light when in solution. Protect from light and oxygen.
Hazards:
H302, H315, H319, H335
InChi:
InChI=1S/C35H58O9/c1-19(2)32-24(7)27(36)18-35(40,44-32)26(9)31(38)25(8)33-28(41-10)14-12-13-20(3)15-22(5)30(37)23(6)16-21(4)17-29(42-11)34(39)43-33/h12-14,16-17,19,22-28,30-33,36-38,40H,15,18H2,1-11H3/b14-12-,20-13+,21-16+,29-17-/t22-,23-,24+,25+,26,27-,28+,30+,31-,32-,33-,35-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
XDHNQDDQEHDUTM-AZJYDCQCSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 88899-55-2. Formula: C35H58O9. MW: 622.8. Bafilomycin A1, a macrolide antibiotic, is a highly potent, selective inhibitor of vacuolar H+-ATPases. Bafilomycin A1 is a potent inhibitor of cellular autophagy either by blocking autophagosome-lysosome fusion or by blocking lysosomal degradation. Bafilomycin A1 has several other biological properties. It induces apoptosis or acts as an ionophore, meaning it can transfer K+ ions across biological membranes. Bafilomycin A1 can induce mitochondrial swelling in the presence of K+ ions, stimulate the oxidation of pyrimidine nucleotides and uncouple oxidative phosphorylation. Inhibition of V-ATPase activity with bafilomycin A1 led to the exacerbation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human monocytes in response to LPS. Bafilomycin A1 also significantly inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication. In cancer, bafilomycin A1 has been shown to inhibit the growth of tumor cells by blocking the acidification of lysosomes. In lysosomal storage disorders, bafilomycin A1 has been shown to promote the clearance of accumulated cellular waste from lysosomes. In neurodegenerative diseases, bafilomycin A1 has been shown to protect neurons from damage.
MDL:
MFCD06795130
Molecular Formula:
C35H58O9
Molecular Weight:
622.8
Other Data:
Note: We recommend not to use ethanol or methanol as solvent whenever possible. In presence of trace amounts of acids both solvents can potentially chemically react with Bafilomycin A1 and cause degradation or esterification of the compound.
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Precautions:
P261, P280, P301, P312, P302, P352, P405
Product Description:
Bafilomycin A1, a macrolide antibiotic, is a highly potent, selective inhibitor of vacuolar H+-ATPases. Bafilomycin A1 is a potent inhibitor of cellular autophagy either by blocking autophagosome-lysosome fusion or by blocking lysosomal degradation. Bafilomycin A1 has several other biological properties. It induces apoptosis or acts as an ionophore, meaning it can transfer K+ ions across biological membranes. Bafilomycin A1 can induce mitochondrial swelling in the presence of K+ ions, stimulate the oxidation of pyrimidine nucleotides and uncouple oxidative phosphorylation. Inhibition of V-ATPase activity with bafilomycin A1 led to the exacerbation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human monocytes in response to LPS. Bafilomycin A1 also significantly inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication. In cancer, bafilomycin A1 has been shown to inhibit the growth of tumor cells by blocking the acidification of lysosomes. In lysosomal storage disorders, bafilomycin A1 has been shown to promote the clearance of accumulated cellular waste from lysosomes. In neurodegenerative diseases, bafilomycin A1 has been shown to protect neurons from damage.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal Word:
Warning
SMILES:
[H][C@@]1(OC(=O)\C=C(OC)\C(C)=C[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C)C\C(C)=C\C=C\[C@@H]1OC)[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)[C@@]1(O)C[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)[C@H](O1)C(C)C
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (100mg/ml), 100% ethanol (5mg/ml) or methanol (5mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Isolated from Streptomyces griseus.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution protect from light at -20°C.
Documents
References
Metabolic products of microorganisms. 224. Bafilomycins, a new group of macrolide antibiotics. Production, isolation, chemical structure and biological activity: G. Werner, et al.; J. Antibiot. 37, 110 (1984) | Bafilomycins: a class of inhibitors of membrane ATPases from microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells: E.J. Bowman, et al.; PNAS 85, 7972 (1988) | Inhibition of osteoclast proton transport by bafilomycin A1 abolishes bone resorption: K. Sundqui, et al.; BBRC 168, 309 (1990) | Kinetic studies of chromaffin granule H+-ATPase and effects of bafilomycin A1: H. Hanada, et al.; BBRC 170, 873 (1990) | Bafilomycin A1 inhibits the targeting of lysosomal acid hydrolases in cultured hepatocytes: K. Oda, et al.; BBRC 178, 369 (1991) | Bafilomycin A1, a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase, inhibits acidification and protein degradation in lysosomes of cultured cells: T. Yoshimori, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 266, 17707 (1991) | Bafilomycin A1, a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase, blocks lysosomal cholesterol trafficking in macrophages: T. Furuchi, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 268, 27345 (1993) | Cell-type and amyloid precursor protein-type specific inhibition of A beta release by bafilomycin A1, a selective inhibitor of vacuolar ATPases: J. Knops, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 270, 2419 (1995) | Autophagy, bafilomycin and cell death: the "a-B-cs" of plecomacrolide-induced neuroprotection: J.J. Shacka, et al.; Autophagy 2, 228 (2006), (Review) | Bafilomycin A1-sensitive pathway is required for the maturation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator: T. Okiyoneda, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1763, 1017 (2006) | Ectopic vesicular neurotransmitter release along sensory axons mediates neurovascular coupling via glial calcium signaling: A. Thyssen, et al.; PNAS 107, 15258 (2010) | Low-dose Bafilomycin attenuates neuronal cell death associated with autophagy-lysosome pathway dysfunction: V.N. Pivtoraiko, et al.; J. Neurochem. 114, 1193 (2010) | Alterations in osteoclast function and phenotype induced by different inhibitors of bone resorption -implications for osteoclast quality: A.V. Neutzsky-Wulff, et al.; BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 11, 109 (2010) | Rapid recycling of Ca2+ between IP3-sensitive stores and lysosomes: C.I. Lopez Sanjurjo, et al.; PLoS One 9, e111275/1 (2014) | Bafilomycin A1 inhibits autophagy and induces apoptosis in MG63 osteosarcoma cells: Z. Xie, et al.; Mol. Med. Rep. 10, 1103 (2014) | Comparison of the chemoimmunotherapeutic effect of doxorubicin and bafilomycin-A1 in mouse neuroblastoma cells: S. Inoue, et al.; Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. Cancer & Chemotherapy 41, 617 (2014) | Suppression of influenza A virus replication in human lung epithelial cells by noncytotoxic concentrations Bafilomycin A1: B. Y, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 308, L270 (2015) | Bafilomycin A1 targets both autophagy and apoptosis pathways in pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: N. Yuan, et al.; Haematologica 100, 345 (2015) | Suppression of influenza A virus replication in human lung epithelial cells by noncytotoxic concentrations Bafilomycin A1: B. Yeganeh, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. 308, L270 (2015) | The protective effect of bafilomycin A1 against cobalt nanoparticle-induced cytotoxity and aseptic inflammation in macrophages in vitro: S. Wang, et al.; Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 169, 94 (2016) | Age-dependent changes in synaptic plasticity enhance tau oligomerization in the mouse hippocampus: T. Kimura, et al.; Acta Neuropathol. Comm. 5, 67 (2017) | Molecular mechanisms of Streptococcus pneumoniae-targeted autophagy via pneumolysin, Golgi-resident Rab41, and Nedd4-1 mediated K63-linked ubiquitination: M. Ogawa, et al.; Cell Microbiol. 20, e12846 (2018) | Proton pumping V-ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin A1 affects Rab7 lysosomal localization and abolishes anterograde trafficking of osteoclast secretory lysosomes: N. Matsumoto & M. Nakanishi-Matsui; BBRC 510, 421 (2019) | Molecular basis of V-ATPase inhibition by bafilomycin A1: R. Wang, et al.; Nat. Commun. 12, 1782 (2021) | Bafilomycin A1 enhances NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human monocytes independent of lysosomal acidification: S. Yu, et al.; FEBS J. 288, 3186 (2021) | Bafilomycin A1 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in a human lung xenograft mouse model: C. Zhang, et al.; Virol. J. 20, 18 (2023)